
The above command will show a small readout of how many files and folders are currently using the temporary directory.
#FINDING DF ROOT FOLDER HOW TO#
If it’s not, head over to and learn how to install it. Note: tree may already be installed on your Linux system. Need a detailed readout of exactly how many files and folders are inside of the temporary directory? Try out the tree command. However, if you’re just looking for a quick rundown of how much space the folder is using, the du command is better to use, as it shows only how much of the temporary directory is occupied (in megabytes,) and nothing more.
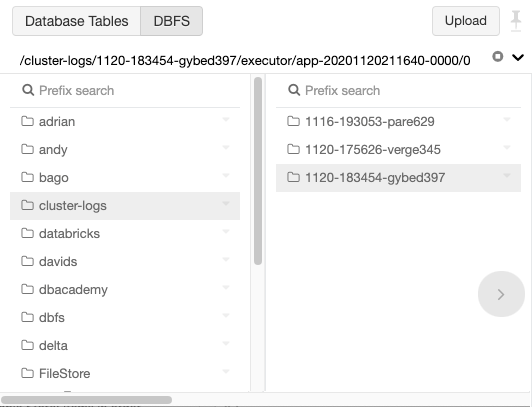
The df command is excellent at showing a detailed readout of the temporary directory. It’ll replace the block readout into plain megabytes and gigabytes, which is much easier to understand. df /tmpĭon’t like the blocks readout? Consider combining the df command along with the “h” command-line switch. Then, with the command-line window open and ready to go, point the du command at the temporary directory to view how much data it is using in blocks. Open up a terminal window by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T or Ctrl + Shift + T on the keyboard. The Df command is excellent at checking the size of the temporary directory on Linux, as it’s a built-in command-line tool that comes with all Linux operating systems. To prevent the temporary directory from filling up in the future, so that there is no need to resort to clearing it manually, here are some quick ways to check the current data usage of the folder. Sometimes, an excess of data can quickly fill up the folder. Many programs and services use it to store temporary data. The temporary directory is an important location on Linux.
#FINDING DF ROOT FOLDER FULL#
Check when Linux temporary folder is full If there is still data in the directory, re-run the command above and try again. Assuming the rm command was successful, nothing will appear.
rm -rf *įrom here, run the ls command once again to see the contents of the temporary directory. This will save time, and make it so that there is no need to write the rm command over and over for each folder and file in the temporary directory. By using a wildcard with the rm command, the Linux command-line will delete every single file and folder at once. Then, run the rm command with the “-rf” switch and a wildcard symbol *. Inside of the temporary directory on your Linux system, run the ls command to view the contents of the folder. With the command-line switched over to root access, move to the “/tmp” with the CD command. Once the command-line window is open, gain root access. You can do this by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T or Ctrl + Alt + Shift + T on the keyboard.

The first step in cleaning out the temporary directory using the rm command is to open up a terminal window. That said, if you haven’t had good luck with Method 1, going this route is the only other option. find /tmp -exec rm -rf + Method 2 – empty directory with rmĭeleting everything out of the temporary directory is best done with method 1, as it avoids using the rm command a whole bunch. If you’d prefer to delete absolutely everything, try this find command instead. find /tmp -type f -deleteīy running the command above, the temporary directory is empty of all files. Now that you’ve gained root access in the terminal use the find command below, combined with the “-delete” switch to empty all files from of the temporary directory. Then, once the command-line window is ready to use, switch from a standard user to the root account by using the su or sudo -s command. To use the find command to clean the Linux temporary folder, start by opening up a terminal window by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T or Ctrl + Shift + T on the keyboard. It can also be used to promptly delete lots of files from any directory - including the one that houses temporary data.
The find command, which is built into all Linux distributions, isn’t just a robust command-line app for Linux that can find files and folders quickly. However, if you’re running a Linux system that doesn’t reboot often, the folder can fill up and cause immense problems. Typically, the size of the temporary folder isn’t an issue, as it clears upon each reboot. The temporary folder on a Linux system has a limited amount of space.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
